Material basics
What is material?
Material is group of shader program codes and arguments used for rendering objects.
For example, if you use forward-shading plugin to use lights, you can make so different rendering result from different parameters.
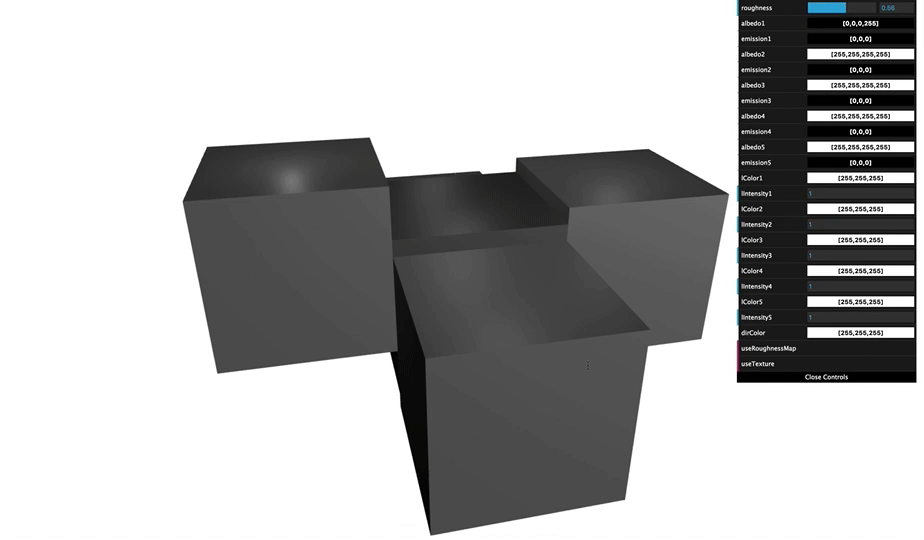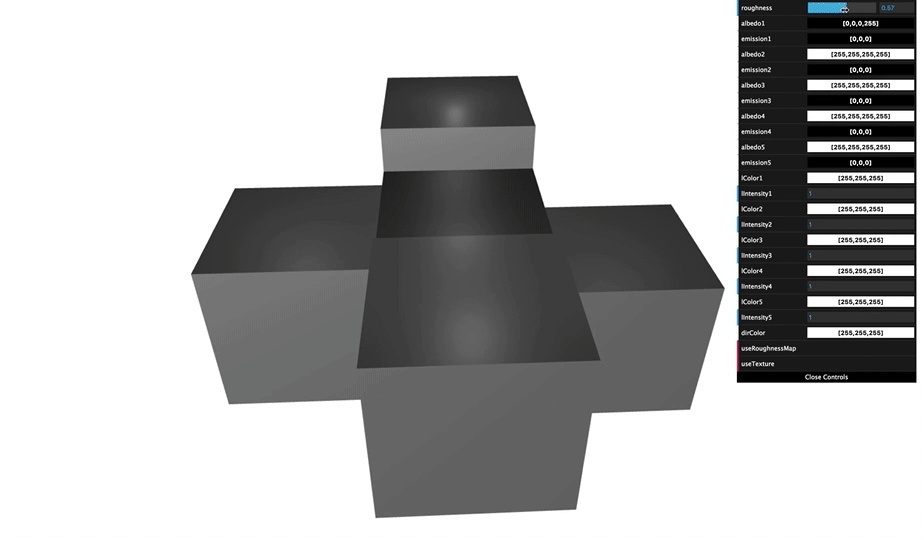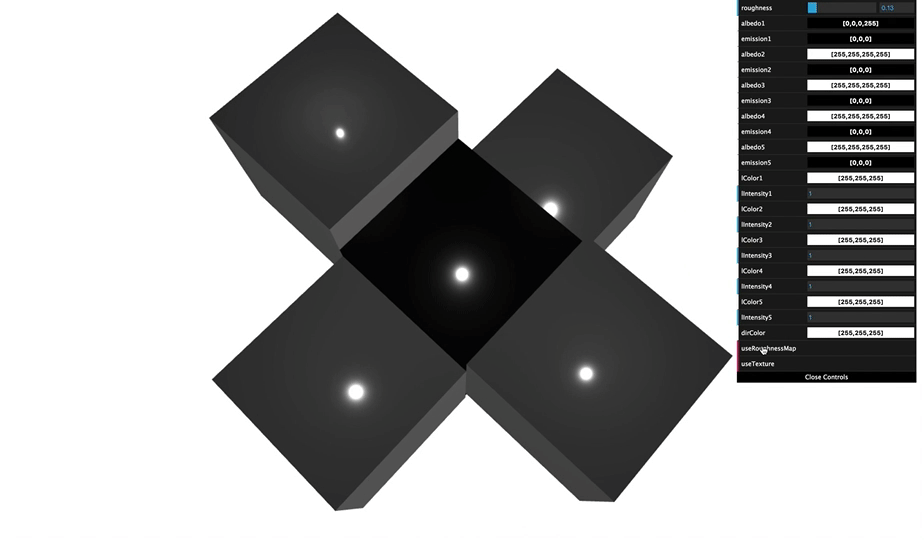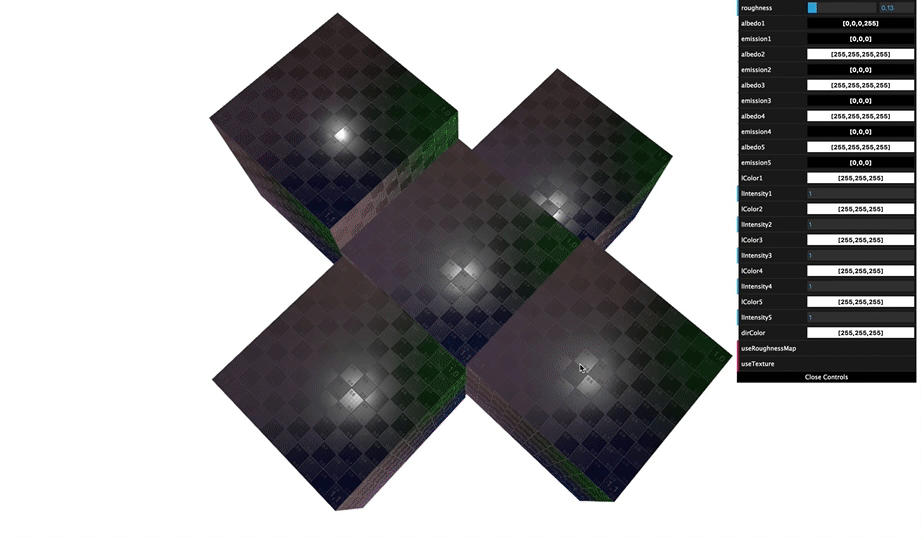
You can see various appearance of cube that was made by changing material arguments.
By understanding material of Grimoire, you can achieve an appearance you want to create.
material attribute on mesh
As we described in tutorial, we can specify color attribute as default.
1 | <mesh geometry="cube" color="yellow"/> |
You need to know there was omitted default value material. If we denote default value of material, it should be following code.
1 | <mesh geometry="cube" material="new(unlit)" color="yellow"/> |
new(unlit) is just a default value of material on MeshRenderer component attached to mesh.
forward-shadingplugin will rewrite default value ofmaterialonMeshRendererFor users can use shader enabling shading by default, if you use
forward-shadingplugin, the plugin will rewrite default value ofmaterial.
The default value will benew(basic)when you use the plugin.
material attribute determine what kind of material arguments (such as color or texture) are available on that tag.
For instance, if you specified new(unlit) on a <mesh> tag, you will be able to specify color and texture attribute on the <mesh>. When you specified new(basic) enabled by linking forward-shading plugin, you will be able to specify roughness , roughnessTexture , albedo and so on.
As you need to know what arguments are available when you want to use javascript function, material parameters are different and depends on what material used.
syntax of material attribute
There are 2 types of syntax is available on material attribute.
${query-to-material}new(${material-name})
new() syntax is very useful if you need to instanciate a <mesh> from javascript because it does not require instanciate the other tags such as material. However, if you have a lot of meshes that have same materials, you should use query syntax. It works more faster than ‘new syntax’.
query syntax on material attribute
You can use “query syntax” of material for sharing material configuration between meshes.
1 | <goml> |
Ensure that you need to specify material arguments on <material> tag not <mesh> tag.
‘new’ syntax on material attribute
When you need to create material for each <mesh>, it is pain to make <material> for each <mesh>.
For these case, you can use “new syntax” of material for creating a material instance for the mesh.
1 | <goml> |
Ensure that you need to specify materials on each <mesh> tags.
Material arguments
Most of materials on Grimoire is created with custom material file .sort. Grimoire will generate attributes for this custom material file by parsing variables of shader code.
Therefore, these arguments are completely depends on what material you need to use.
But, this is argument list of official shaders.
unlit shader
This is default value of material(if you didn’t link forward-shading plugin).
This shader not supports shadings. Just for painting with single color or attach texture.
arguments
- color(Color4)・・・solid color to draw the mesh
- texture(Texture)・・・a texture to attach to mesh
basic shader
This is a shader enabled by forward-shading plugin. If you need to use shading, you would need to use this shader.
arguments
- albedo(Color4)・・・baseColor on the mesh
- texture(Texture)・・・baseColor of texture on the mesh(This color will be used with albedo by multiplying)
- roughness(float)・・・0 to 1 value to specify how the mesh is rough.
- roughnessTexture(Texture)・・・a texture containing roughness info. The texture needs to contain roughness in R channel.
- metalic(float)・・・0 to 1 value to specify how the mesh is metalic.
- emission(Color3)・・・the color of the mesh emitting. This color is not affected by shades.
Your custom material
Of course you can make your own material. You should read Custom material(WIP) document for making your own material.
Even our official materials are written in same way as I wrote in the Custom material document.